1.2. Dispersion and Differential Entropy¶
1.2.1. Dispersion Entropy \(H_{de}(X)\)¶
1.2.1.1. Background¶
Unlike usual entropy, Dispersion Entropy take the temporal dependency into accounts, same as Sample Entropy and Aproximate Entropy. It is Embeding Based Entropy function. The idea of Dispersion is almost same as Sample and Aproximate, which is to extract Embeddings, estimate their distribuation and compute entropy. However, there is a fine detail that make dispersion entropy more usuful.
First, is to map the distribuation original signal to uniform (using CDF), then divide them into n-classes. This is same as done for quantization process of any normally distributed signal, such as speech. In quantization, this mapping helps to minimize the quantization error, by assiging small quantization steps for samples with high density and large for low. Think this in a way, if in a signal, large number of samples belongs to a range (-0.1, 0.1), near to zero, your almost all the embeddings will have at least one value that is in that range. CDF mapping will avoid that. In this python implimentation, we have included other mapping functions, which are commonly used in speech processing, i.e. A-Law, and µ-Law, with parameter A and µ to control the mapping.
Second, it allows to extract Embedding with delay factor, i.e. if delay is 2, an embeding is continues samples skiping everu other sample. which is kind of decimation. This helps if your signal is sampled at very high sampling frequecy, i.e. super smooth in local region. Consider you hhave a signal with very high smapling rate, then many of the continues samples will have similar values, which will lead to have a very high number of contant embeddings.
Third, actuall not so much of third, but an alternative to deal with signal with very high sampling rate, is by scale factor, which is nothing but a decimator.
1.2.1.2. An Example¶
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import spkit as sp
np.random.seed(1)
x1, fs = sp.data.optical_sample(sample=1)
t = np.arange(len(x1))/fs
H_de1, prob1 = sp.dispersion_entropy(x1,classes=10,scale=1)
print('DE of x1 = ',H_de1)
2.271749287746759
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import spkit as sp
X,ch_names = sp.load_data.eegSample()
fs=128
#filtering
Xf = sp.filter_X(X,band=[1,20],btype='bandpass',verbose=0)
Xi = Xf[:,0].copy() # only one channel
de,prob,patterns_dict,_,_= sp.dispersion_entropy(Xi,classes=10, scale=1, emb_dim=2, delay=1,return_all=True)
print(de)
2.271749287746759
See also
Important Note on Log base check following note
Important Note: Log base
The Entropy here is computed as \(-\sum p(x)log_e (p(x))\) , natural log. To convert to log2, simply divide the value with np.log(2)
de/np.log(2)
3.2774414315752844
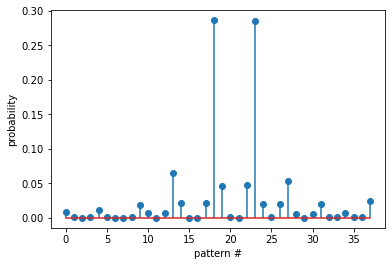
Probability of all the patterns found
plt.stem(prob)
plt.xlabel('pattern #')
plt.ylabel('probability')
plt.show()
Pattern dictionary
patterns_dict
{(1, 1): 18,
(1, 2): 2,
(1, 4): 1,
(2, 1): 2,
(2, 2): 23,
(2, 3): 2,
(2, 5): 1,
(3, 1): 1,
(3, 2): 2,
top 10 patters
PP = np.array([list(k)+[patterns_dict[k]] for k in patterns_dict])
idx = np.argsort(PP[:,-1])[::-1]
PP[idx[:10],:-1]
array([[ 5, 5],
[ 6, 6],
[ 4, 4],
[ 7, 7],
[ 6, 5],
[ 5, 6],
[10, 10],
[ 4, 5],
[ 5, 4],
[ 8, 8]], dtype=int64)

1.2.1.3. Embedding dimension 4¶
de,prob,patterns_dict,_,_= sp.dispersion_entropy(Xi,classes=20, scale=1, emb_dim=4, delay=1,return_all=True)
de
4.86637389336799
top 10 patters
PP = np.array([list(k)+[patterns_dict[k]] for k in patterns_dict])
idx = np.argsort(PP[:,-1])[::-1]
PP[idx[:10],:-1]
array([[10, 10, 10, 10],
[11, 11, 11, 11],
[12, 12, 12, 12],
[ 9, 9, 9, 9],
[11, 11, 10, 10],
[10, 10, 11, 11],
[11, 11, 11, 10],
[10, 10, 10, 11],
[10, 11, 11, 11],
[11, 10, 10, 10]], dtype=int64)
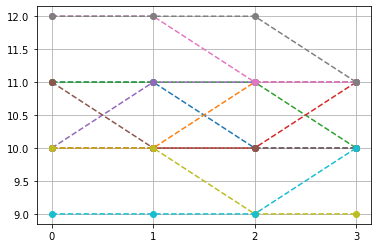
top-10, non-constant pattern
Ptop = np.array(list(PP[idx,:-1]))
idx2 = np.where(np.sum(np.abs(Ptop-Ptop.mean(1)[:,None]),1)>0)[0]
plt.plot(Ptop[idx2[:10]].T,'--o')
plt.xticks([0,1,2,3])
plt.grid()
plt.show()

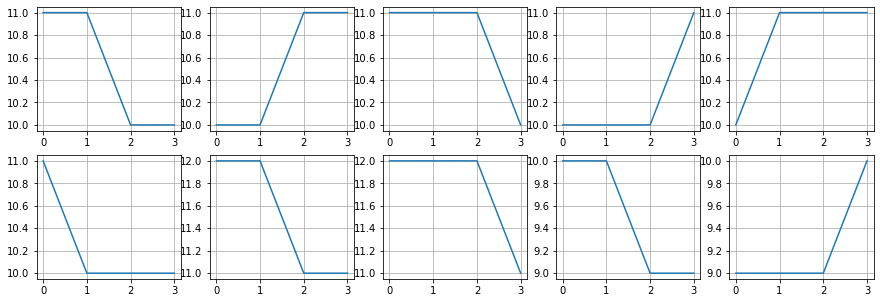
plt.figure(figsize=(15,5))
for i in range(10):
plt.subplot(2,5,i+1)
plt.plot(Ptop[idx2[i]])
plt.grid()
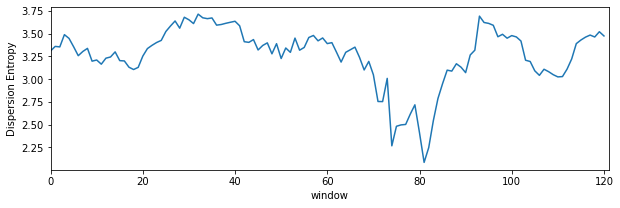
1.2.1.4. Dispersion Entropy with sliding window¶
de_temporal = []
win = np.arange(128)
while win[-1]<Xi.shape[0]:
de,_ = sp.dispersion_entropy(Xi[win],classes=10, scale=1, emb_dim=2, delay=1,return_all=False)
win+=16
de_temporal.append(de)x
plt.figure(figsize=(10,3))
plt.plot(de_temporal)
plt.xlim([0,len(de_temporal)])
plt.xlabel('window')
plt.ylabel('Dispersion Entropy')
plt.show()
1.2.2. Multi-scale Dispersion Entropy¶
1.2.2.1. Dispersion Entropy multiscale¶
for scl in [1,2,3,5,10,20,30]:
de,_ = sp.dispersion_entropy(Xi,classes=10, scale=scl, emb_dim=2, delay=1,return_all=False)
print(f'Sacle: {scl}, \t: DE: {de}')
Sacle: 1, : DE: 2.271749287746759
Sacle: 2, : DE: 2.5456280627759336
Sacle: 3, : DE: 2.6984938704051236
Sacle: 5, : DE: 2.682837351130069
Sacle: 10, : DE: 2.5585556625642476
Sacle: 20, : DE: 2.7480275694000103
Sacle: 30, : DE: 2.4767472897625806
de,_ = sp.dispersion_entropy_multiscale_refined(Xi,classes=10, scales=[1, 2, 3, 4, 5], emb_dim=2, delay=1)
print(de)
2.543855087400606

1.2.3. Dispersion Entropy & Shannon Entropy¶
1.2.4. Dispersion Entropy & Sample Entropy¶
1.2.5. Differential Entropy Functions \(H_{\partial}(\cdot)\)¶
Differential Entropy \(H_{\partial}(X)\)
Differential Entropy of Normally distribuated Multivariant X
for
\[x ∼ N(μ,Σ)\]entropy in nats
\[H_{\partial}(x) = (1/2)ln|Σ| + (1/2)n + (n/2)ln(2π)\]\(H_{\partial}(X)\)
\((1/2)n + (n/2)ln(2π)\) => are constant values for fixed dimension
1.2.6. Differential Entropy \(H_{\partial}(X)\)¶
Differential Entropy of Normally distribuated Multivariant X
\(H_{\partial}(X)\)
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import spkit as sp
x0, fs = sp.data.optical_sample(sample=3)
t = np.arange(len(x0))/fs
x1 = x0 + 0.5*np.random.randn(len(t))
# create multi-dimensional space signals
X0 = sp.signal_delayed_space(x0,emb_dim=3,delay=2)
X1 = sp.signal_delayed_space(x1,emb_dim=3,delay=2)
# Compute Differential Entropy
Hd0 = sp.entropy_differential(X0)
Hd1 = sp.entropy_differential(X1)
print('Differential Entropy')
print(' - x0: ',Hd0)
print(' - x1: ',Hd1)
# Or Compute directly - Compute Differential Entropy
Hd0 = sp.entropy_differential(x0,is_multidim=False,emb_dim=3, delay=2)
Hd1 = sp.entropy_differential(x1,is_multidim=False,emb_dim=3, delay=2)
print('Differential Entropy')
print(' - x0: ',Hd0)
print(' - x1: ',Hd1)
1.2.7. Self-Conditional Entropy \(H_{\partial}(X_{i+1}|X_{i})\)¶
Self-Conditional Entropy \(H_{\partial}(X_{i+1}|X_i)\)
Self-Conditional Entropy
Information of \(X(i+1)\) given \(X(i)\)
\[H_{\partial}(X_{i+1}|X_i) = H_{\partial}(X_{i+1}, X_i) - H_{\partial}(X_i)\]using:: .. math:: H(X|Y) = H(X, Y) - H(Y)
import numpy as np
import spkit as sp
x, fs = sp.data.optical_sample(sample=3)
#x = sp.add_noise(x,snr_db=20)
X = sp.signal_delayed_space(x,emb_dim=5,delay=2)
H_x1x = sp.entropy_diff_cond_self(X, present_first=True)
print('Self-Conditional Entropy')
print(f' H(X(i+1)|X(i)) = {H_x1x}')
1.2.8. Conditional Entropy \(H_{\partial}(X_{i+1}|X_{i},Y_{i})\)¶
Conditional Entropy \(H_{\partial}(X_{i+1}|X_i,Y_i)\)
Conditional Entropy
Information of \(X(i+1)\) given \(X(i)\) and \(Y(i)\)
\[H_{\partial}(X_{i+1}|X_i,Y_i) = H(X_{i+1},X_i,Y_i) - H(X_i,Y_i)\]
#sp.entropy_diff_cond
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import spkit as sp
X, fs, ch_names = sp.data.eeg_sample_14ch()
X = X - X.mean(1)[:, None]
X1 = sp.signal_delayed_space(X[:,0].copy(),emb_dim=5,delay=2)
Y1 = sp.signal_delayed_space(X[:,2].copy(),emb_dim=5,delay=2)
Y2 = sp.add_noise(Y1,snr_db=0)
H_xy1 = sp.entropy_diff_cond(X1,Y1,present_first=True)
H_xy2 = sp.entropy_diff_cond(X1,Y2,present_first=True)
H_y1x = sp.entropy_diff_cond(Y1,X1,present_first=True)
H_y2x = sp.entropy_diff_cond(Y2,X1,present_first=True)
print('Conditional Entropy')
print(f'- H(X1|Y1) = {H_xy1}')
print(f'- H(X1|Y2) = {H_xy2}')
print(f'- H(Y1|X1) = {H_y1x}')
print(f'- H(Y2|X1) = {H_y2x}')
1.2.9. Joint Entropy \(H_{\partial}(X,Y)\)¶
Differential Joint Entropy with
\[H_{\partial}(X,Y)\]
# Example 1
#sp.entropy_diff_joint
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import spkit as sp
X, fs, ch_names = sp.data.eeg_sample_14ch()
X = X - X.mean(1)[:, None]
X1 = sp.signal_delayed_space(X[:,0].copy(),emb_dim=5,delay=2)
Y1 = sp.signal_delayed_space(X[:,2].copy(),emb_dim=5,delay=2)
Y2 = sp.add_noise(Y1,snr_db=0)
H_xy1 = sp.entropy_diff_joint(X1,Y1)
H_xy2 = sp.entropy_diff_joint(X1,Y2)
print('Conditional Entropy')
print(f'- H(X1,Y1) = {H_xy1}')
print(f'- H(X1,Y2) = {H_xy2}')
#############################
# Example 2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import spkit as sp
X, fs, ch_names = sp.data.eeg_sample_14ch()
X = X - X.mean(1)[:, None]
x1,y1 = X[:,0].copy(),X[:,2].copy()
#x1 = x1[:,None]
#y1 = y1[:,None]
y2 = sp.add_noise(y1,snr_db=0)
H_xy1 = sp.entropy_diff_joint(x1,y1)
H_xy2 = sp.entropy_diff_joint(x1,y2)
print('Conditional Entropy')
print(f'- H(X1,Y1) = {H_xy1}')
print(f'- H(X1,Y2) = {H_xy2}')
Joint-Conditional Entropy \(H_{\partial}(X_{i+1},Y_{i+1}|X_i,Y_i)\)
Joint-Conditional Entropy
\[H_{\partial}(X_{i+1},Y_{i+1}|X_i,Y_i) = H(X_{i+1},Y_{i+1},X_i,Y_i) - H(X_i,Y_i)\]
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import spkit as sp
X, fs, ch_names = sp.data.eeg_sample_14ch()
X = X - X.mean(1)[:, None]
# Example 1
X1 = sp.signal_delayed_space(X[:,0].copy(),emb_dim=5,delay=2)
Y1 = sp.signal_delayed_space(X[:,2].copy(),emb_dim=5,delay=2)
Y2 = sp.add_noise(Y1,snr_db=0)
H_xy1 = sp.entropy_diff_joint_cond(X1,Y1)
H_xy2 = sp.entropy_diff_joint_cond(X1,Y2)
print('Conditional Entropy')
print(f'- H(X1(i+1),Y1(i+1) | X1(i),Y1(i)) = {H_xy1}')
print(f'- H(X1(i+1),Y2(i+1) | X1(i),Y2(i)) = {H_xy2}')
1.2.10. Self-Mutual Information \(I_{\partial}(X_{i+1}|X_{i})\)¶
#sp.mutual_info_diff_self
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import spkit as sp
X, fs, ch_names = sp.data.eeg_sample_14ch()
X = X - X.mean(1)[:, None]
# Example 1
X1 = sp.signal_delayed_space(X[:,0].copy(),emb_dim=5,delay=2)
Y1 = sp.add_noise(X1,snr_db=0)
I_x1x = sp.mutual_info_diff_self(X1)
I_y1y = sp.mutual_info_diff_self(Y1)
print('Self-Mutual Information')
print(f'- I(X(i+1)| X(i)) = {I_x1x}')
print(f'- I(Y(i+1)| Y(i)) = {I_y1y}')
1.2.11. Mutual Information \(I_{\partial}(X,Y)\)¶
#sp.mutual_info_diff
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import spkit as sp
X, fs, ch_names = sp.data.eeg_sample_14ch()
X = X - X.mean(1)[:, None]
# Example 1
X1 = sp.signal_delayed_space(X[:,0].copy(),emb_dim=5,delay=2)
Y1 = sp.signal_delayed_space(X[:,2].copy(),emb_dim=5,delay=2)
Y2 = sp.add_noise(Y1,snr_db=0)
I_xy1 = sp.mutual_info_diff(X1,Y1)
I_xy2 = sp.mutual_info_diff(X1,Y2)
print('Mutual-Information')
print(f'- I(X1,Y1) = {I_xy1}')
print(f'- I(X1,Y2) = {I_xy2}')
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Multivariate_normal_distribution Gokhale, DV; Ahmed, NA; Res, BC; Piscataway, NJ (May 1989). “Entropy Expressions and Their Estimators for Multivariate Distributions”. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory. 35 (3): 688–692. doi:10.1109/18.30996.
References
Click for more details
¶





